Motor Insulation Class | Motor Insulation Class for VFD | Induction Motor Insulation Class | 3 Phase Induction Motor Insulation Class
Electric motors rely on insulation to prevent electrical arcing and short circuits from occurring within the motor. Depending on the intended application, different insulation materials and systems are used to provide the necessary protection. Motor insulation is categorized into classes based on the temperature rating of the insulation materials. The most common motor insulation classes are Class A, B, F, H, and N.
Class A Insulation:
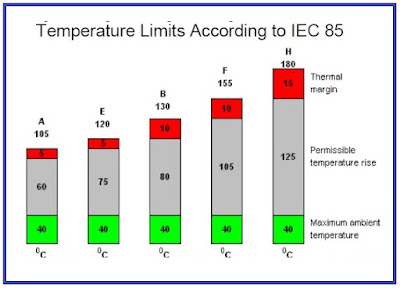
This insulation class is rated for a maximum operating temperature of 105°C. It uses materials such as cotton, silk, paper, and other organic materials that have been impregnated with a varnish or resin. These materials provide good dielectric strength and are cost-effective, but they are not particularly durable and can break down over time.
Class B Insulation:
This insulation class is rated for a maximum operating temperature of 130°C. It is similar to Class A insulation but uses slightly more durable materials, such as mica, glass fibers, and epoxy resins. These materials are more resistant to thermal stress and have better thermal conductivity, but they are more expensive than Class A insulation.
Class F Insulation:
This insulation class is rated for a maximum operating temperature of 155°C. It uses materials such as aramid fibers, polyester, and epoxy resins that have been reinforced with glass fibers or other strengthening agents. Class F insulation provides better thermal and mechanical properties than Class A and B insulation, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Class H Insulation:
This insulation class is rated for a maximum operating temperature of 180°C. It uses materials such as silicone, polyesterimide, and polyimide that have been reinforced with glass fibers or other strengthening agents. Class H insulation provides excellent thermal and mechanical properties, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Class N Insulation:
This insulation class is rated for a maximum operating temperature of 200°C. It uses materials such as ceramic fibers and silicone resins that have been reinforced with glass fibers or other strengthening agents. Class N insulation provides the highest thermal and mechanical properties of all the insulation classes, making it suitable for the most demanding high-temperature applications.
In addition to these main insulation classes, there are also specialty insulation systems that are used for specific applications. For example, motors that operate in hazardous environments may use explosion-proof insulation that is designed to prevent sparks from igniting flammable materials. Similarly, motors that are exposed to moisture or other environmental hazards may use specialized coatings or encapsulation materials to protect the insulation from damage. Ultimately, the selection of motor insulation materials and systems depends on the specific requirements of the motor and the environment in which it will be used.
Motor Insulation Class for VFD
When selecting a motor for use with a variable frequency drive (VFD), it is important to consider the motor insulation class. The insulation class of a motor determines the maximum temperature that the motor winding insulation can withstand.
The recommended insulation class for a motor used with a VFD depends on the switching frequency of the drive. In general, the higher the switching frequency of the drive, the higher the insulation class required for the motor.
For VFDs with switching frequencies up to 4 kHz, a motor with Class F insulation is typically recommended. For VFDs with switching frequencies above 4 kHz, a motor with Class H insulation is recommended.
It is important to note that using a motor with lower insulation class than recommended for a particular VFD can result in premature insulation breakdown and motor failure. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully match the motor and VFD specifications to ensure proper operation and longevity of the motor.
Motor Insulation Components
Varnish:
Insulating Paper:
Insulating Varnished Cloth (IVC):
Insulating Sleeving:
Binding Tapes:
Epoxy:
A motor winding insulation tester
It is a device used to measure the insulation resistance of the windings in electric motors, generators, transformers, and other electrical equipment. This is important because a low insulation resistance can indicate a potential breakdown or short circuit in the equipment, which can lead to a variety of problems, including equipment failure, power outages, and electrical hazards.
There are several methods used to test the insulation resistance of motor windings, including:
Megger test:
This is a commonly used test method that involves applying a high voltage DC signal to the motor winding and measuring the resulting current flow. The insulation resistance is calculated by dividing the applied voltage by the measured current. Megger testers are available in a range of voltages and are designed to provide accurate and reliable insulation resistance measurements.
Polarization index test:
This test involves measuring the insulation resistance of a motor winding at two different time intervals, typically 10 minutes and 1 minute. The ratio of the two measurements is known as the polarization index, which provides an indication of the condition of the insulation. A high polarization index indicates good insulation, while a low value indicates a potential problem.
Step voltage test:
This test involves applying a series of increasing voltages to the motor winding and measuring the resulting current flow at each voltage level. The data is plotted on a graph, and the insulation resistance is calculated based on the slope of the curve.
High-potential test:
This is a more specialized test that involves applying a very high voltage, typically 2-3 times the rated voltage of the motor, to the winding and measuring the resulting current flow. The test is used to detect any weak spots in the insulation that could lead to a breakdown or short circuit.
Motor winding insulation testers are widely available and can be purchased or rented from electrical equipment suppliers or test and measurement equipment providers. The specific test method used will depend on the equipment being tested, the desired level of accuracy, and other factors. It is important to follow proper safety procedures when conducting insulation resistance tests, as high voltages can be dangerous if not handled correctly.




Post a Comment