Cable Nomenclature | Aluminium Cables | Power Cables | Types Of Electric Cables | Different Types Of Cables | DC Power Cables | Screen Cable Types
Cable nomenclaturer refers to the naming or identification of different types of cables based on their construction, function, and application This can include things like the type of conductor used, the insulation material, the voltage rating, and many other factors. By understanding cable nomenclature, it is possible to quickly and accurately identify the right cables for any given application
Cable Nomenclature | Aluminium Cables | Power Cables | Types Of Electric Cables | Different Types Of Cables | DC Power Cables
- Cable nomenclature refers to the naming conventions used for identifying different types of cables.
- Cables are typically named based on their composition, construction, and intended use.
- The most common types of cables include power cables, data cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables.
- Power cables are used for transmitting electrical power from a source to a device or system. They are typically made of copper or aluminium conductors and are rated for different levels of voltage and current.
- Data cables are used for transmitting digital signals between devices or systems. They can be categorized based on their speed and transmission distance, with common types including Ethernet, USB, and HDMI cables.
- Coaxial cables are used for transmitting high-frequency signals such as television and radio signals. They are composed of a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and a shield.
- Fiber optic cables use light to transmit signals over long distances at high speeds. They are made of a core of glass or plastic fibers surrounded by protective layers.
Coaxial Cable
This is a type of cable that
has a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulating layer, which in
turn is surrounded by a braided shield and an outer jacket. It is commonly used
for transmitting video and high-frequency signals. Examples of coaxial cables
include RG-6 and RG-59.
Examples of coaxial cables include:
RG-6:
RG-59:
This is a thinner and more flexible
coaxial cable used for shorter cable runs and in home audio and video
applications.
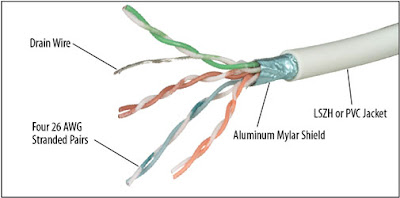
Twisted Pair Cable
This type of cable
consists of two or more insulated wires twisted together to reduce
electromagnetic interference. It is commonly used for transmitting data and telecommunications
signals. Examples of twisted pair cables include Category 5e and Category 6.
Category 5e:
This is a type of twisted pair
cable that supports data transfer rates up to 1 Gbps. It is commonly used in
home and small office networks.
Category 6:
This is a higher-performance twisted pair cable that supports data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps. It is commonly used in larger networks and data centers.
Fiber Optic Cable
This is a cable that
uses optical fibers to transmit data through light signals. It is commonly used
for long-distance communication and high-speed internet connections. Examples
of fiber optic cables include single-mode and multi-mode cables.
Examples of fiber optic cables include:
Single-mode fiber:
This type of fiber optic
cable has a smaller core size and is designed for longer distances and higher
bandwidths. It is commonly used in long-haul telecommunications and data center
applications.
Multimode fiber:
This type of fiber optic cable has a larger core size and is designed for shorter distances and lower bandwidths. It is commonly used in local area networks and data center applications.
Shielded Cable
This is a cable that has a
grounded shield around the inner conductor to reduce electromagnetic
interference. It is commonly used for applications that require high
reliability and low noise. Examples of shielded cables include STP (shielded
twisted pair) and FTP (foiled twisted pair).
Examples of shielded cables include:
STP (shielded twisted pair):
This is a type
of twisted pair cable with an additional shielding layer around the conductors.
It is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications where there is a
lot of electromagnetic interference.
FTP (foiled twisted pair):
This is a type
of twisted pair cable with a foil shielding layer around the conductors. It is
commonly used in audio and video applications where noise reduction is
critical.
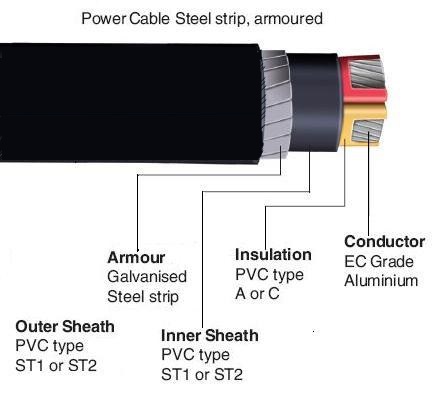
Power Cable
This type of cable is designed
to carry electrical power from one point to another. It is commonly used in
residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Examples of power cables
include THHN, NM, and UF cables.
Examples of power cables include:
THHN:
This is a type of wire with a
thermoplastic insulation that is resistant to heat and moisture. It is commonly
used in residential and commercial electrical systems.
NM (non-metallic):
This is a type of
electrical cable that is used in residential and commercial construction. It
consists of two or more insulated conductors inside a plastic jacket.
UF (underground feeder):
This is a type of electrical cable that is designed for underground use. It has a moisture-resistant jacket and can be buried directly in the ground.
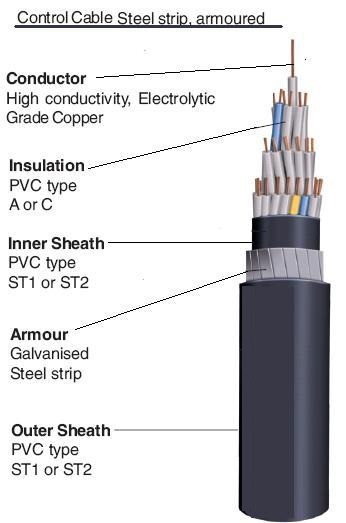
Control Cable
This is a type of cable used
to transmit electrical signals from one device to another. It is commonly used
for industrial automation and process control applications. Examples of control
cables include instrumentation cables and cable tray cables.
Examples of control cables include:
Instrumentation cable:
This is a type of
control cable that is used for transmitting low-voltage signals from sensors
and other control devices to controllers or monitoring equipment. It is
commonly used in chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and other
industrial applications.
Cable tray cable:
This is a type of control
cable that is designed for installation in cable trays. It is commonly used in
commercial and industrial buildings for power and control applications.
VFD cable:
This is a type of control cable that is used for variable frequency drives (VFDs). It is designed to reduce electrical noise and provide better performance in VFD applications.
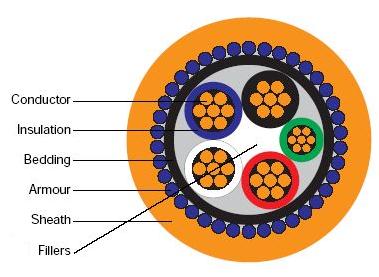
Different Types of Screen Cables
Braided screen cable:
This type of cable has a braided metal screen that surrounds the conductors. The braid is typically made of multiple wires that are woven together to form a tight mesh.
Foil Screen cable:
This type of cable has a thin layer of metal foil wrapped around the conductors. The foil is typically made of aluminum, and is bonded to the insulation to provide a continuous shield.
Combination Screen cable:
This type of cable combines both braided and foil screens for maximum EMI protection.
Screen Cable
When selecting a screen cable, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application, including the level of EMI protection needed and the operating environment. It is also important to properly terminate and ground the cable to ensure effective EMI protection.
Shielding offers the benefits of significantly improved pair-to-pair crosstalk performance, alien crosstalk performance, and noise immunity that cannot be matched by any other cabling design strategy. (Application- Analog Signal handling
Cat-6 Cable
Category 6, Cat-6 network cabling is used as the cabling infrastructure for 10BASE-T (Ethernet), 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet), 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet, or GbE) and 10GBASE-T (10-Gigabit Ethernet, or 10 GbE) networks
What is the full form of XLPE Cable
XLPE means for cross-linked polyethylene. This and other cross-linked synthetic materials, of which EPR (ethylene propylene rubber) is a notable example, are being increasingly used as cable insulants for a wide range of voltages.
XLPE cable is suitable for voltage ranges from
But it can typically range from 300 volts up to 500 kV or higher. XLPE cables are widely used for power transmission and distribution, as well as in industrial and commercial applications, due to their excellent electrical and mechanical properties, high durability, and resistance to environmental factors.

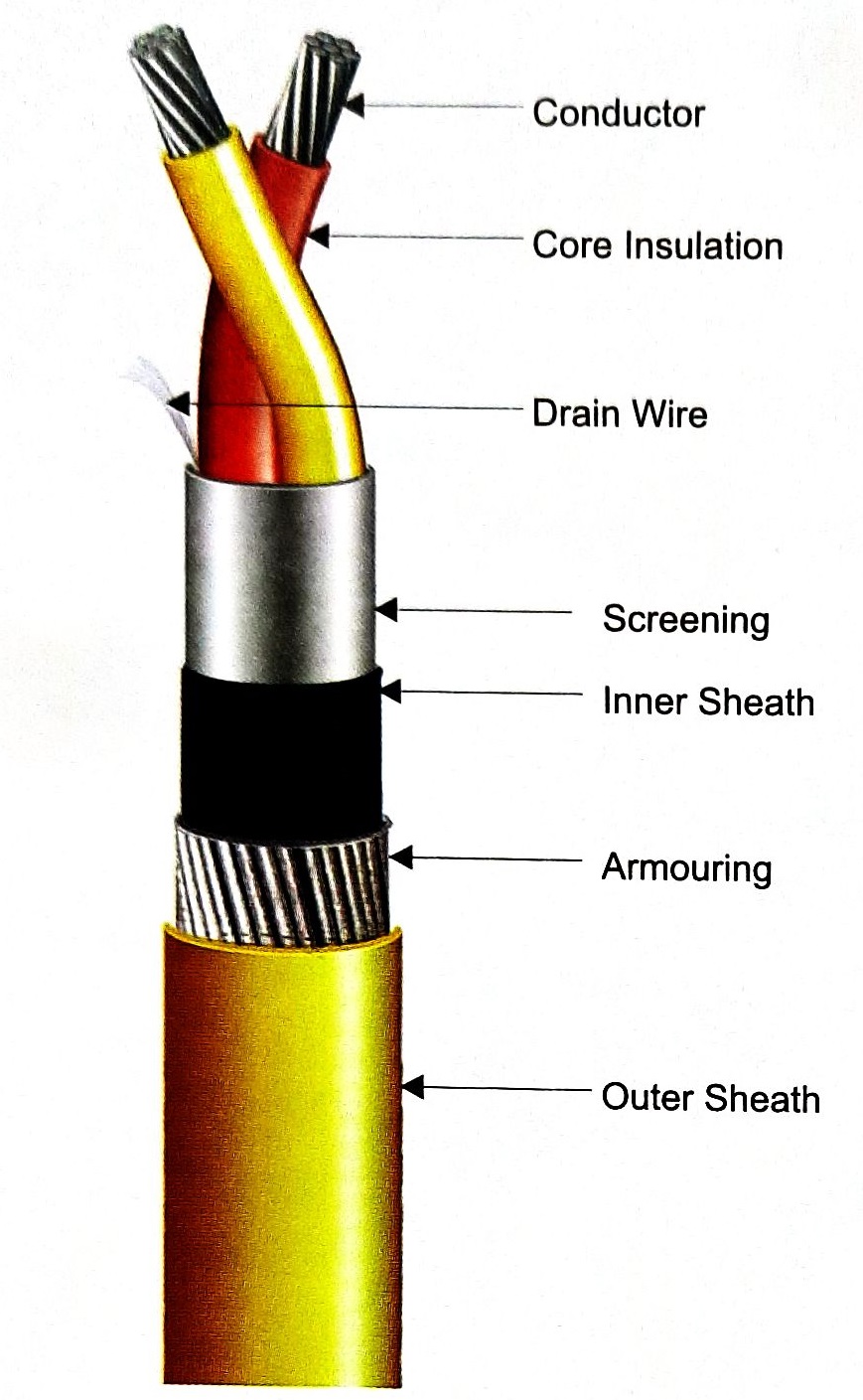





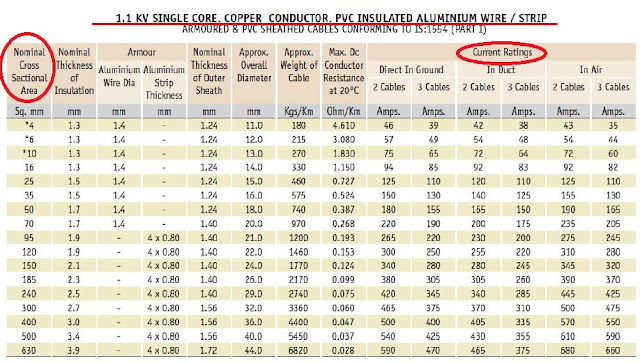






Thank you for the visual aid on the different types of cabling. I now know what the electrician is talking about when he comes to install the cabling into our new house. They use a lot of nomenclatures that can be confusing to understand. I understand why electricians now should install the cables in your home. http://www.holdenselectrical.com.au/about-us
ReplyDeleteGreat blog ! I really like your blog. Your blog is very informative. Thanks for sharing such a useful blog. Paraflex is leading Best Top Aluminium Wire Manufacturers in India in India, certified by BIS, ISO, NSIC, SSI. We provide you housing wire, industrial wire , aluminium cable, cctv cable etc. of best quality and all cables are available at the best price.
ReplyDeleteElektroarbeiten sind eine ernsthafte Haushaltsreparatur, die Sie nur dann selbst durchführen können, wenn Sie eine Elektrikerausbildung absolviert und ein Arbeitszertifikat erworben haben. Wenn Sie Probleme mit der elektrischen Verkabelung Ihres Hauses haben, können Sie durch die Einstellung eines guten Elektrikers vor Unfällen und weiteren Haushaltsproblemen geschützt werden. Nachfolgend sind die Elemente und einige Tipps aufgeführt, die Sie berücksichtigen sollten, um den richtigen Elektriker zu finden, der Ihre Anforderungen erfüllt. stromausfall notdienst
ReplyDeleteTycon Cables is a recognized brand of Submersible Cables Manufacturers in India. we have created a highly skilled technical team and stringent quality controls to ensure that every meter of cable leaving our premises is of highest quality. The manufacturing design of these cable depends on the factors to achieve the highest possible degree of reliability and safety in the area where it would be installed. OurMulitcore Cables is very power saving, reliable, flexible, tough, and can work in wet conditions for a longer period.
ReplyDelete