Voltage Limiter | Voltage Limiter Circuit | Voltage Limiter using op amp | Voltage Limiter circuit using diode and a resistor
1. Introduction to Voltage Limiter
A voltage limiter, also known as a surge protector, is a device that limits voltage spikes in electrical systems. Voltage spikes can cause significant damage to electronic devices and appliances, leading to equipment failure or even fires. Voltage limiters are designed to protect against these voltage surges and ensure the safety and longevity of your equipment.
2. Understanding Voltage Surges
Voltage surges, also known as transients, are sudden increases in voltage that can occur in electrical systems. These surges can be caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or the switching on and off of large electrical equipment. Voltage surges can cause damage to electronic devices and appliances, including power supplies, computers, televisions, and refrigerators. Voltage limiters are designed to protect against these voltage surges and ensure the safety of your equipment.
3. How Voltage Limiters Work
Voltage limiters work by detecting the voltage spikes in electrical systems and redirecting the excess voltage away from the equipment. The voltage limiter acts as a pathway for the excess voltage to be redirected, ensuring that the voltage remains at a safe level for the equipment.
4. Types of Voltage Limiters
There are several types of voltage limiters available, including gas discharge tubes, metal oxide varistors, silicon avalanche diodes, and transient voltage suppressors.
4.1 Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs)
Gas discharge tubes, or GDTs, are one of the oldest types of voltage limiters. They work by using a small gap between two electrodes filled with gas. When the voltage across the gap exceeds a certain level, the gas becomes ionized, and the voltage is redirected away from the equipment.
4.2 Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs)
Metal oxide varistors, or MOVs, are one of the most common types of voltage limiters. They work by using a metal oxide disc to absorb excess voltage. When the voltage exceeds a certain level, the metal oxide disc becomes conductive, and the excess voltage is redirected away from the equipment.
4.3 Silicon Avalanche Diodes (SADs)
Silicon avalanche diodes, or SADs, are another type of voltage limiter. They work by using a p-n junction that becomes conductive when the voltage exceeds a certain level. The excess voltage is redirected away from the equipment, ensuring that the voltage remains at a safe level.
4.4 Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVSs)
Transient voltage suppressors, or TVSs, are a newer type of voltage limiter that is becoming more common. They work by using a semiconducting material that becomes conductive when the voltage exceeds a certain level. The excess voltage is then redirected away from the equipment, ensuring that the voltage remains at a safe level.
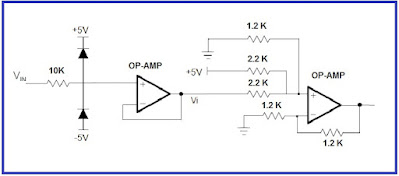
4.5 Voltage limiter using op amp
An op amp can be used as a voltage follower, which means that the output voltage will be equal to the input voltage. By connecting a zener diode in series with the op amp output, the op amp will limit the output voltage to the zener diode's breakdown voltage. This effectively limits the voltage that can pass through the circuit and protects the electronic equipment from voltage surges.
Another way to use an op amp as a voltage limiter is by using it as a comparator. A comparator compares two input voltages and produces an output voltage that is either high or low, depending on the relative magnitudes of the input voltages. By connecting one input of the comparator to a fixed reference voltage and the other input to the input voltage that needs to be limited, the comparator can be used to limit the output voltage to a safe level.
4.6 Voltage limiter circuit using diode and a resistor
A voltage limiter circuit using a diode and a resistor is a simple and effective way to limit the amount of voltage that can pass through a circuit. The circuit works by using a diode and a resistor in series with the load to limit the output voltage to a safe level.
The diode in the circuit is connected in reverse bias, which means that it will only conduct current when the voltage across it exceeds a certain threshold. When the voltage across the diode exceeds this threshold, it begins to conduct, which limits the amount of voltage that can pass through the circuit. By choosing the appropriate diode and resistor values, the circuit can be designed to limit the output voltage to a safe level.
The resistor in the circuit is used to limit the current flowing through the diode and prevent it from being damaged by excess current. The resistor value is chosen based on the maximum current that the diode can handle, and the desired output voltage.
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Voltage Limiter
When choosing a voltage limiter, there are several factors that you should consider. These include the maximum clamping voltage, response time, current rating, and application.
5.1 Maximum Clamping Voltage
The maximum clamping voltage is the maximum voltage that the voltage limiter can handle. You should choose a voltage limiter with a maximum clamping voltage that is higher than the maximum voltage of your electrical system.
5.2 Response Time
The response time is the time it takes for the voltage limiter to react to a voltage surge. You should choose a voltage limiter with a fast response time to ensure that your equipment is protected from voltage surges.
5.3 Current Rating
The current rating is the maximum amount of current that the voltage limiter can handle. You should choose a voltage limiter with a current rating that is higher than the maximum current of your electrical system.
5.4 Application
The application refers to the type of equipment that you are trying to protect. Different types of equipment may require different types of voltage limiters. You should choose a voltage limiter that is specifically designed for the type of equipment you are trying to protect.
6. Benefits of Voltage Limiters
There are several benefits to using voltage limiters. These include:
- Protection of electronic devices and appliances from voltage surges
- Prevention of equipment failure and fires
- Extended lifespan of electronic devices and appliances
- Peace of mind knowing that your equipment is protected
7. Installation and Maintenance of Voltage Limiters
Voltage limiters are relatively easy to install and maintain. To install a voltage limiter, you simply need to connect it to your electrical system. To maintain a voltage limiter, you should periodically check it to ensure that it is still functioning properly.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, voltage limiters are an essential component of any electrical system. They protect your electronic devices and appliances from voltage surges, ensuring their safety and longevity. When choosing a voltage limiter, it is important to consider factors such as the maximum clamping voltage, response time, current rating, and application. By using a voltage limiter, you can enjoy peace of mind knowing that your equipment is protected.
FAQs
What is a voltage limiter?
A voltage limiter is an electronic device that protects electronic devices and appliances from voltage surges. It works by limiting the amount of voltage that can pass through a circuit to a safe level.
How do voltage limiters work?
Voltage limiters work by either blocking or redirecting excess voltage away from electronic devices and appliances. They typically use one of several technologies, such as metal oxide varistors, gas discharge tubes, or transient voltage suppressors.
What are the different types of voltage limiters?
There are several types of voltage limiters, including metal oxide varistors, gas discharge tubes, transient voltage suppressors, and zener diodes.
How do I choose the right voltage limiter for my equipment?
When choosing a voltage limiter, it is important to consider factors such as the maximum clamping voltage, response time, current rating, and application. You should choose a voltage limiter with a maximum clamping voltage that is higher than the maximum voltage of your electrical system and a current rating that is higher than the maximum current of your electrical system. You should also choose a voltage limiter that is specifically designed for the type of equipment you are trying to protect.
How do I install and maintain a voltage limiter?
Voltage limiters are relatively easy to install and maintain. To install a voltage limiter, you simply need to connect it to your electrical system. To maintain a voltage limiter, you should periodically check it to ensure that it is still functioning properly.






Post a Comment