DCS Full Form | What is DCS Systems | DCS Systems | What is DCS vs PLC? | How does DCS work? | Where are DCS used? | What are the types of DCS? | What are the main components of DCS?
DCS Full Form is Distributed Control Systems are advanced computer-based control systems used to monitor and control industrial processes. DCS systems are used in industries such as chemical plants, oil refineries, and power stations. They offer a distributed architecture that enables control functions to be spread across multiple computers, making them more reliable and easier to maintain. DCS systems can handle complex processes and control a large number of inputs and outputs from various field devices such as sensors, actuators, and motors. These systems allow for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, providing operators with accurate and up-to-date information about the process. By optimizing process control and reducing downtime, DCS systems can improve process efficiency and reduce costs
DCS Full Form | What is DCS Systems | DCS Systems
- DCS is a computer-based control system used to control and monitor industrial processes such as chemical plants, power stations, and oil refineries.
- DCS is designed to handle complex processes and control a large number of inputs and outputs from various field devices, such as sensors, actuators, and motors.
- DCS uses a distributed architecture, which means that the control functions are spread out over multiple computers, making the system more reliable and easier to maintain.
- DCS typically consists of a central control room where operators can monitor and control the process, as well as remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that perform control functions in the field.
- DCS allows for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, providing operators with accurate and up-to-date information about the process.
- DCS can improve process efficiency and reduce costs by optimizing process control and reducing downtime.
- DCS can be easily integrated with other systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to provide a complete view of the industrial process.
- DCS provides advanced diagnostic and maintenance features, allowing operators to quickly identify and resolve problems in the process.
- DCS systems are highly customizable, allowing for the creation of custom control strategies and the integration of third-party software.
The key advantage of DCSs is that they divide up the control tasks among multiple distributed systems; if any single part of the system should fail, the plant could keep operating. DCS systems also introduced the concept of data networking, thereby allowing hard wiring each control point, adding flexibility, and reducing the cost of making changes in the production process. The DCS has capacity for processing large number of I/O points.
What are the types of DCS?
• Conventional DCS: a pure “process-only” control system. Typically purchased from one vendor and arranged into categories; small, medium and large.
• PLC-based DCS: a network of PLCs used to perform the task of conventional DCS and programmable functionality when required.
• Hybrid DCS: Performs both process and sequential control.
• Open DCS System: A Field-Bus control. Advantages include: low wiring costs, less failure, lower expansion costs and multi-vendor interoperability. DCS and PLCs can be more interconnected.
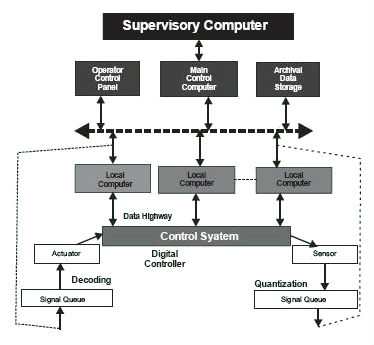
Distributed Control System is a flexible framework to implement control strategies and readjust controller parameter for the software. The configuration of DCS is as shown in following figure
DCS networks are centralized dynamic system in which the control elements are not central in location but are distributed throughout the system with each components subsystem controlled by one or more controllers. It controls manufacturing processes that are continuous or batch oriented. The example of such process can be oil refining,
petrochemicals, central power generation, food and beverage manufacturing, cement
production, steel making and paper making.
Typical DCS consists of functionally distributed digital controllers capable of executing from 1 to 256 or more regulatory controlled loops in one control box. DCS may employ one or several workstations and can be configured at the workstations or by an offline personal computer by using twisted pair, co-axial or fiber optic networking cables. Prime advantage of DCS is digital communication between controllers and supervisory computers with focus on the networks, which provide the all-important lines of communication. The communication system has to incorporate specific functions such as determinism and redundancy or process application.
DCS brought distributed intelligence to the plant and established the presence of the computers and microprocessors in process control. However, it still did not provide the openness necessary to unify plant resource requirements. As a result suppliers began to adopt Ethernet based network with their own proprietary protocol layers.
In DCS a single process controlled computer is connected to all sensors and actuators. While the sensors and actuators come from many different vendors each devise has to be configured to work with the central process control computer.
What are the main components of DCS?
FCS (Field Control Station):It controls the process. All the instruments and interlocks created by software reside in the memory of the FCS. All the field instruments like transmitters and control valves are wired to the FCS.
OPS (Operator Station) / HIS (Human Interface Station) : Used to monitor the process and to operate various instruments.
Communication Bus: Used to communicate between the FCS and the OPS
Modes of Computer control
1) Manual
2) Automatic
PID with local set point
3) Supervisory
PID with remote set point (supervisory)
4) Advanced
Common DCS systems
1. Yokogawa - CS 3000
2. Yokogawa - Centum Excel
3. Yokogawa - Micro Excel
4. ABB - Freelance 2000
5. Fisher - Rosemount - Delta V field
6. Fisher - Rosemount RS3
7. Honeywell - GUS
8. Honeywell - TDC 3000
9. Fox boro - I/A series
10. Moore - APACS
What is DCS importance? | Advantages of DCS
• Redundancy is available at various levels.
• Information regarding the process is presented to the user in various formats.
• Control function is distributed among multiple CPUs (Field Control Stations). Hence failure of one FCS does not affect the entire plant.
• Provision & modification of interlocks are very flexible and simple.
• Instruments and interlocks are created through software.
• Alternate quickly among standard control strategies and readjust controller parameters in software.
• Access a large amount of current information from the data highway.
• Monitoring trends of past process conditions.
• Readily install new on-line measurements together with local computers.
• A sight full engineer can use the flexibility of the framework to implement his latest controller design ideas on the host computer.
• Field wiring is considerably less.
• Maintenance and trouble shooting becomes very easy.
• Cost effective in the long run.
Is DCS better than SCADA? | Differences Between SCADA and DCS
In the past, SCADA and DCS were separate entities, however with the advancement in technology, it sometimes appears to be similar. The solutions, process orientation and connectivity are what make these systems contrasting entities. The key differences between the two systems include:
a) Goals / Solutions: A DCS is usually more process-oriented in contrast to SCADA, which focuses on gathering data. DCS scans and concentrates on the controlled process and presents the information to the operators. SCADA, on the other hand, concentrates mainly on the control center as well as the operators. The remote equipment is mainly used to collect data even though it can be used to carry out other multifaceted process controls.
b) Functionality: It is crucial to note that in a DCS system, the operator has a closed-loop control at the PCS/RTU levels. However, closed-loop control is unavailable in a SCADA system. In its place, you can access the control via the HMI, using human as supervisory control. In this regard, most DCS systems today have integrated HMI and supervisory facilities, DB connectivity as well as all basic facilities that come with SCADA system. Due to the time limitations and urgency, control is done without engaging Human in control flow at the PLC/RTU.
c) Connectivity: A DCS operator station is usually linked to its I/O via the local wiring, networks and FieldBus. The operator makes a request directly to the field I/O whenever he wants to get information and gets a response for the same. This means that field events can directly disrupt the system and counsel the operator. On the other hand, whenever field communication fails, SCADA has to operate reasonably. Its main concern of a SCADA system operation is the quality of the data that is shown to the operator. In short, a DCS system is principally concerned with the process trends while a SCADA system is driven by the process events
What is DCS vs PLC?
DCS (Distributed Control System) and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) are both computer-based control systems used in industrial applications, but they differ in their architecture, capabilities, and functions.
DCS is designed to control and monitor large-scale industrial processes, such as chemical plants, power stations, and oil refineries. DCS uses a distributed architecture, with the control functions spread out over multiple computers. DCS systems are typically used to control a large number of inputs and outputs from various field devices, such as sensors, actuators, and motors. DCS systems can handle complex processes and provide real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes.
PLC, on the other hand, is designed to control a single machine or a small process. PLC is a stand-alone system that operates independently and is not connected to other PLCs. PLCs are typically used for discrete manufacturing processes, such as assembling products on a factory line or controlling a conveyor belt. PLCs are programmable and can be customized to control a specific process or machine.






Join Our Organization to Learn #Project Based and job based #PLC #Scada #Automation #Training in #Noida.. Improve your skill in #PLCScada Call us 9953489987 or Quick query Click on DIAC .
ReplyDeleteThank you for this informative blog. We provide What is Inventory Management which helps you streamline and automate your distribution network, making the process more efficient and helps you in tracking the Goods Inventory and increase visibility over the complete Supply Chain cycle.
ReplyDeleteBest PLC training Institute help aspirants to learn Industrial automation, PLC, SCADA, HMI by DIAC and we help to find your dream job in core industry. Call now 9953489987.
ReplyDelete