AC Servo Motors | AC Servo Motors Working Principle | Application Of AC Servo Motor | AC Servo Motor is basically a
AC servo motors are an essential component of any servo system, converting electrical signals into precise motion control. In this article, we'll cover the various types of AC servo motors, their typical ratings, and tips for selecting the right motor for your application. AC servo motors are high-performance electric motors that are commonly used in various applications, including robotics, machine tools, and industrial automation. The term "servo" refers to a closed-loop control system that uses feedback to maintain the desired position, speed, or torque of a motor.
AC
Servo Motors | AC Servo Motors Working Principle
- AC servo motors are high-performance electric motors commonly used in robotics,
machine tools, and industrial automation.
- These
motors use a closed-loop control system to maintain precise control over
position, speed, and torque.
- The
motor consists of a stator, rotor, and feedback device such as an encoder or
resolver.
- The
stator contains stationary windings that produce a magnetic field when an AC
voltage is applied, while the rotor has permanent magnets or windings that
interact with the stator's magnetic field to produce a rotating motion.
- The
feedback device monitors the position or speed of the rotor and sends signals
to the servo amplifier.
- The
servo amplifier adjusts the motor's input voltage and frequency to maintain the
desired output, based on the input signal from the controller and the feedback
signal from the motor.
- AC
servo motors offer high accuracy, repeatability, and dynamic performance,
making them suitable for CNC machines, robotics, and industrial automation.
- They
also have a high power-to-weight ratio, which makes them ideal for applications
that require high acceleration and deceleration rates.
AC Servo Motor is basically a
An AC servo motor is basically a type of electric motor that uses AC power to drive its operation. It is designed to provide precise
control over position, speed, and torque, making it ideal for a wide range of industrial applications.
AC servo motors typically include a feedback device such as an encoder or resolver, which provides information about the motor's position and velocity to a control system. The control system uses this information to adjust the AC voltage and frequency applied to the motor, allowing it to maintain precise control over its operation.
AC Servo Motors Working Principle
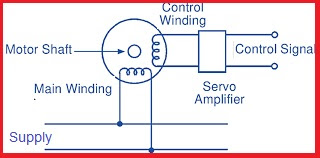
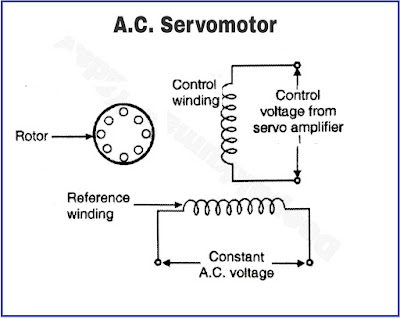
The working principle of an AC servo motor involves a combination of electrical and mechanical components. The motor is typically composed of a stator, rotor, and feedback device such as an encoder or resolver. The stator contains the stationary windings that produce a magnetic field when an AC voltage is applied. The rotor, which is mounted on a shaft, has permanent magnets or windings that interact with the stator's magnetic field to produce a rotating motion.
The
feedback device monitors the position or speed of the rotor and sends signals
to the servo amplifier, which adjusts the motor's input voltage and frequency
to maintain the desired output. The servo amplifier receives the input signal
from the controller, which specifies the desired position or speed, and
compares it with the feedback signal from the motor. If there is a difference
between the two signals, the servo amplifier adjusts the motor's input voltage
and frequency to minimize the error and maintain the desired output.
The key advantage of an AC servo motor is its ability to provide precise and dynamic control over the motor's position, speed, and torque. This makes it an ideal choice for applications that require high accuracy and repeatability, such as CNC machines, robotics, and industrial automation. Additionally, AC servo motors offer a high power-to-weight ratio, which makes them suitable for applications that require high acceleration and deceleration rates.
Types of AC Servo Motors:
There are various types of AC servo motors available in the market, each with specific features and applications. Some of the most commonly used types of AC servo motors are:
Brushless AC Servo Motors - This type of AC servo motor uses electronic commutation instead of brushes to achieve precise motion control. It is a popular choice for high-precision applications that require low maintenance and high efficiency.
AC Servo Motors with Encoders - This type of AC servo motor includes an encoder that provides feedback to the drive to ensure precise motion control. It is ideal for applications that require accurate positioning and speed control.
Positional Rotation Servo Motors: These servo motors are designed to rotate to a specific position and maintain that position until directed to move again. They are commonly used in applications that require precision and accuracy, such as robotics, automation, and CNC machines.
Continuous Rotation Servo Motors: Unlike positional rotation servo motors, continuous rotation servo motors are designed to rotate continuously in either direction. They are often used in applications that require constant motion, such as conveyor belts and robotic arms.
Linear Servo Motors: As the name suggests, linear servo motors provide motion in a straight line rather than rotation. They are commonly used in applications that require high precision and accuracy, such as CNC machines and medical devices.
Typical Ratings of AC Servo Motors:
AC servo motors are typically rated based on several factors, including:
Torque Rating - The torque rating of AC servo motors varies depending on the specific application. Typical torque ratings range from 0.1 Nm to 500 Nm.
Speed Rating - AC servo motors are rated for maximum speed. Typical speed ratings range from 1,000 RPM to 10,000 RPM.
Power Rating - AC servo motors are rated for maximum power output. Typical power ratings range from 50W to 5kW.
Feedback Resolution - AC servo motors with encoders are rated for feedback resolution, which determines the accuracy of motion control. Typical feedback resolution ratings range from 1,000 to 10,000 counts per revolution.
Frame Size - AC servo motors are available in different frame sizes, ranging from small sizes for low-torque applications to larger sizes for high-torque applications.
Tips for Selecting the Right AC Servo Motor:
Selecting the right AC servo motor for your application is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Some tips for selecting the right AC servo motor include:
- Determine the torque and speed requirements of your application.
- Choose a motor with a power rating that is suitable for your application.
- Consider the feedback resolution required for accurate motion control.
- Select a motor with a frame size that fits your application's mechanical requirements.
Type Numbers for AC Servo Motors:
Different manufacturers use different type numbers to identify their AC servo motors. Some examples of type numbers for AC servo motors are:
Mitsubishi HC-SFS102 - A brushless AC servo motor with a torque rating of 1.0 Nm and a speed rating of 3,000 RPM.
Yaskawa SGMJV-08 - A brushless AC servo motor with an encoder and a torque rating of 0.32 Nm.
Application Of AC
Servo Motor | AC Servo Motor
Application | AC Servo Motor Applications
AC
servo motors are used in a wide range of industrial applications where precise
and rapid motion control is required. Here are some of the common applications
of AC servo motors:
1 Robotics: AC servo motors are widely used in robotics for precise control over the movement of robot arms, joints, and end-effectors. They can provide high torque at low speeds and maintain precise position control, making them ideal for applications such as welding, painting, and assembly.
CNC machines: AC servo motors are commonly used in computer numerical control (CNC) machines such as milling machines, lathes, and routers. They provide accurate and repeatable control over the movement of cutting tools and workpieces, resulting in high-quality machining.
2 Printing presses: AC servo motors are used in printing presses for precise control over the motion of printing plates, ink rollers, and paper feeders. They ensure accurate registration and alignment of printing plates, resulting in high-quality printing.
4 Automated manufacturing equipment: AC servo motors are used in a variety of automated manufacturing equipment such as pick-and-place machines, material handling systems, and packaging machines. They provide fast and precise motion control, resulting in high-speed and efficient production.
5 Medical equipment: AC servo motors are used in medical equipment such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and robotic surgery systems. They provide precise and accurate control over the movement of medical instruments and equipment, resulting in improved patient outcomes.ker HPLA - A linear AC servo motor with a maximum speed of 5 m/s and a force rating of 1000 N.
Typical Ratings of AC Servo motor cables:
AC
servo motor cables are typically rated based on several factors, including:
Voltage and Current Ratings - The voltage and current ratings of AC servo motor cables vary depending on the specific application. Typical voltage ratings range from 300V to 600V, while current ratings range from 2A to 10A.
Temperature Rating - AC servo motor cables are rated for the maximum operating temperature. Typical temperature ratings range from -40°C to +80°C.
Flex Life - AC servo motor cables are designed to withstand constant motion and bending. Flex life ratings typically range from 3 million to 20 million cycles.
Shielding - AC servo motor cables are shielded to protect against electromagnetic interference. Typical shielding types include braided shielding and foil shielding.
Connector Type - AC servo motor cables are available in different connector types, including circular connectors, rectangular connectors, and hybrid connectors.
Tips for Selecting the Right AC Servo Cable:
Selecting the right AC servo cable for your application is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Some tips for selecting the right AC servo cable include:
- Determine the voltage and current requirements of your servo system.
- Select a cable with a temperature rating that is suitable for your application.
- Choose a cable with a high flex life rating to withstand constant motion and bending.
- Consider the type of shielding required to protect against electromagnetic interference.
- Select a connector type that is compatible with your servo system.
Type Numbers for AC Servo motor cables:
Different
manufacturers use different type numbers to identify their AC servo motor
cables. Some examples of type numbers for AC servo motor cables are:
- Belden 8760 - A single-cable design AC servo cable rated for 600V and 10A.
- Lapp Ölflex Servo FD 7YSLCY-JB - A multi-cable design AC servo cable rated for 300V and 6A.
- igus CF29.UL.H - A hybrid design AC servo cable rated for 600V and 8A.
Fault Diagnosis for AC Servo Motors:
Here
are some common faults that can occur in AC servo motors, along with their
potential causes:
Noisy operation - This can be caused by worn bearings, damaged rotor or stator, or loose connections.
Overheating - This can be caused by excessive load, high ambient temperature, or insufficient ventilation.
Vibration - This can be caused by misalignment, unbalanced load, or worn bearings.
Loss of torque - This can be caused by a damaged rotor or stator, faulty resolver or encoder, or worn bearings.
Electrical faults - These can be caused by short circuits, open circuits, or ground faults in the motor wiring or control circuit.
To diagnose faults in AC servo motors, it is essential to perform regular inspections, such as checking for abnormal noise, vibration, or overheating during operation. Also, checking the motor wiring and connections can help identify electrical faults.
Maintenance for AC Servo Motors:
Following are typical maintenance procedures for AC servo motors:
Lubrication - AC servo motors require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear. The frequency of lubrication depends on the specific motor application and operating conditions.
Cleaning - AC servo motors should be kept clean and free of debris, dust, and other contaminants. Regular cleaning can prevent damage to the motor bearings, rotor, and stator.
Resolver or encoder replacement - AC servo motors require regular resolver or encoder replacement to maintain optimal performance. The frequency of replacement depends on the specific motor application and operating conditions.
Bearing replacement - AC servo motors require periodic bearing replacement to maintain optimal performance and prevent damage to other motor components.
Electrical component inspection - Regular inspection of motor wiring, connectors, and other electrical components can prevent electrical faults and ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Proper fault diagnosis and maintenance are critical to ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of AC servo motors. By following the typical fault diagnosis and maintenance procedures outlined in this article, you can identify and address faults in AC servo motors and ensure the best possible performance from your servo system. Regular maintenance can prevent costly downtime and extend the life of your AC servo motors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an AC servo motor and how does it work?
What is the difference between AC and DC servo motors?
What are the three types of servo motors?
Positional Rotation Servo Motors: These servo motors are designed to rotate to a specific position and maintain that position until directed to move again. They are commonly used in applications that require precision and accuracy, such as robotics, automation, and CNC machines.
Continuous Rotation Servo Motors: Unlike positional rotation servo motors, continuous rotation servo motors are designed to rotate continuously in either direction. They are often used in applications that require constant motion, such as conveyor belts and robotic arms.
Linear Servo Motors: As the name suggests, linear servo motors provide motion in a straight line rather than rotation. They are commonly used in applications that require high precision and accuracy, such as CNC machines and medical devices.
What are the five main parts of a servo motor?
The five main parts of a servo motor are the rotor, stator, encoder, feedback mechanism, and control circuit. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor that generates torque and movement, while the stator is the stationary part that interacts with the rotor to generate the magnetic field. The encoder is a device that measures the position of the rotor and provides feedback to the control circuit, which adjusts the current supplied to the motor to maintain the desired position.
What is a servo used for?
Servo motors are used in a wide range of industrial and manufacturing applications to provide precise control over motion. They are often used in robotics, automation, CNC machines, medical devices, and other applications that require high precision and accuracy. Servo motors are known for their reliability, speed, and accuracy, making them ideal for applications that require precise motion control.
What is the difference between a servo motor and a stepper motor?
A servo motor provides continuous motion, while a stepper motor provides precise incremental motion.






Post a Comment