Solar Energy | Solar Energy Diagram | Solar Power Generator | Solar Power Panel | Solar Power Calculator | Solar Power System | Solar Power For Home | Solar Power Plant
If you are looking for a sustainable and renewable source of energy, then solar energy might be the solution for you. A solar power system generates electricity from sunlight, which can power your home or business while reducing your carbon footprint. In this article, we will guide you through the different types of solar energy system, Solar Energy Diagram its benefit, and how to choose the right system for our needs.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
Solar power is generated through the use of solar panels, which absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
Types of Solar Power Systems
There are three types of solar power systems: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the right system for you depends on energy needs and budget. Here are some examples and models of different types of solar power systems:
Grid-Tied Solar Power Systems
Grid-tied solar power systems are the most common type of solar power system. They are connected to the electric grid and can feed excess electricity back into the grid. This allows homeowners and businesses to earn credits or even make money by selling their excess electricity to the utility company.
An example of a grid-tied solar power system is the Enphase IQ7 Microinverter System. This system includes microinverters that are connected to each individual solar panel, allowing for greater efficiency and reliability.
Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
Off-grid solar power systems are not connected to the electric grid and rely on batteries to store excess electricity for use when the sun is not shining. These systems are ideal for remote locations where grid power is not available.
An example of an off-grid solar power system is the Goal Zero Yeti 3000 Lithium Portable Power Station. This system includes solar panels, a battery bank, and an inverter, and can provide power for appliances and electronics even in remote locations.
Hybrid Solar Power Systems
Hybrid solar power systems combine the benefits of grid-tied and off-grid systems. They are connected to the electric grid but also have batteries to provide backup power in case of a power outage.
An example of a hybrid solar power system is the Tesla Powerwall. This system includes a battery bank and can be used to store excess electricity for use during peak hours or as backup power during a blackout.
Portable Solar Power Systems
Portable solar power systems are small, lightweight systems that are ideal for camping, hiking, or other outdoor activities. They typically include solar panels, a battery, and an inverter, and can be easily transported.
An example of a portable solar power system is the Renogy Phoenix Portable Generator All-in-One Solar Kit. This system includes a foldable solar panel, a battery, and an inverter, and can be used to power small appliances and electronics while on the go.
Solar Energy Diagram | Components of a Solar Power System
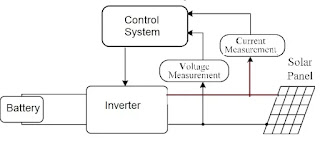
A solar power system is made up of several components, namely solar panels, inverters, batteries, and charge controllers. each of which plays a crucial role in converting sunlight into usable electricity. Understanding the components of a solar power system can help you choose the right system for your needs.
Solar Power Panels
Solar power panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of multiple interconnected solar cells, which are responsible for capturing sunlight and transforming it into usable energy. Solar power panels have become increasingly popular in recent years, as they provide a sustainable and eco-friendly way of generating electricity.
Solar Power Panels are the most visible component of a solar power system. They are made up of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. The size and number of solar panels you need will depend on your energy needs and the amount of sunlight your location receives.
There are two main types of solar panels: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single silicon crystal and are more efficient but also more expensive. Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon crystals and are less expensive but also less efficient.
Inverter
The inverter is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power your home or business. There are two main types of inverters: string inverters and microinverters.
String inverters are connected to multiple solar panels and convert the electricity from all of the panels at once. Microinverters are connected to each individual solar panel and convert the electricity from each panel separately. Microinverters are more expensive but also more efficient and reliable.
Batteries
Batteries are not necessary for a grid-tied solar power system, but they can provide backup power in case of a power outage. They can also be used to store excess electricity generated by your solar panels for use when the sun is not shining.
There are several types of batteries that can be used in a solar power system, including lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and flow batteries. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Charge Controller
The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the batteries. It ensures that the batteries are not overcharged or undercharged, which can damage the batteries or reduce their lifespan.
There are two main types of charge controllers: PWM (pulse width modulation) and MPPT (maximum power point tracking). MPPT charge controllers are more expensive but also more efficient and can generate up to 30% more electricity than PWM charge controllers.
Monitoring System
A monitoring system allows you to track the performance of your solar power system in real-time. It can provide information on the amount of electricity being generated, the amount of electricity being used, and the status of the batteries.
There are several types of monitoring systems, including online monitoring systems and mobile apps. These systems can also alert you to any problems with your system, such as a decrease in performance or a malfunctioning component.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Solar Power System
Choosing a solar power system requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure that you get the best system for your needs. Here are some of the key factors to consider when selecting a solar power system:
Energy needs:
The first step in selecting a solar power system is to determine your energy needs. This involves calculating how much energy you use on a daily basis, and how much of that energy you want to generate with solar power.
System size:
Once you know your energy needs, you can determine the size of the solar power system you need to meet those needs. The size of your system will depend on the amount of energy you want to generate, the amount of sunlight your location receives, and other factors.
Location:
The amount of sunlight your location receives is a critical factor in determining the size and type of solar power system you need. If you live in an area with a lot of shade or cloudy weather, you may need a larger system to generate the same amount of energy as someone living in a sunnier location.
Orientation and tilt:
The orientation and tilt of your solar panels can affect their efficiency and how much energy they generate. Ideally, your panels should face south and be tilted at an angle that maximizes sun exposure.
Panel efficiency:
The efficiency of your solar panels is an important factor in determining the size of your solar power system. More efficient panels can generate more energy per square foot of space, which means you may need fewer panels to meet your energy needs.
Quality and durability:
It's important to choose high-quality, durable solar panels and components to ensure that your system lasts for many years and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
Cost:
Solar power systems can be expensive, so it's important to consider the cost of the system and how long it will take to recoup your investment through energy savings.
Installation and Maintenance of Solar Power Systems
Installation and maintenance of solar power systems are crucial for ensuring that they operate efficiently and effectively. Proper installation and regular maintenance can also help extend the lifespan of the system and maximize its energy output. Here are some important considerations for the installation and maintenance of solar power systems:
Installation:
Site Selection: The first step in installing a solar power system is to select a suitable site. The site should be free from shading, have sufficient space for the solar panels, and be located in an area that receives adequate sunlight.
Mounting: The solar panels need to be mounted securely to a structure or support system that can withstand high winds and other environmental factors. The angle and orientation of the panels should also be optimized for maximum energy production.
Wiring: The wiring of the solar power system should be carefully planned and installed to minimize energy losses and ensure safety. Proper grounding and circuit protection are also critical to prevent electrical hazards.
Inverter Installation: The inverter is an important component of the solar power system that converts DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used in homes or businesses. The inverter should be installed in a cool, dry, and ventilated location to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Maintenance:
Regular Cleaning: Solar panels can accumulate dirt, debris, and other contaminants that can reduce their energy output. Regular cleaning with water and a soft brush or cloth can help maintain their efficiency.
System Monitoring: Monitoring the performance of the solar power system can help detect any issues or inefficiencies. This can be done through a monitoring system or by checking the output of the system regularly.
Inverter Maintenance: Inverters may need periodic maintenance or replacement to ensure that they are operating at peak performance. This may involve cleaning, firmware updates, or replacement of worn-out parts.
Battery Maintenance: If the solar power system includes battery storage, regular maintenance may be required to ensure that the batteries are functioning properly. This may involve checking the battery voltage, electrolyte levels, and other factors.
Solar Power Calculator
A solar power calculator based on load can help to determine the size of solar power system need to meet your energy needs. following formula can be used to calculate the required solar power system size:
Solar power system size (in watts) = Total daily energy consumption (in watt-hours) / Peak sun hours per day
To use this formula, you'll need to calculate your total daily energy consumption by adding up the watt-hours of all the devices you plan to power with your solar power system. For example, if you plan to power a refrigerator that uses 1200 watts for 6 hours per day, your daily energy consumption for the refrigerator would be 7200 watt-hours (1200 watts x 6 hours).
Next, you'll need to determine the peak sun hours per day in your location. This refers to the number of hours per day that the sun is strong enough to produce energy at its maximum capacity. You can find this information for your location online or by using a solar insolation map. As an example, let's say your location has an average of 5 peak sun hours per day.
Using these values, you can calculate the required solar power system size using the formula:
Solar power system size = 7200 watt-hours / 5 peak sun hours per day = 1440 watts
So, in this example, you would need a solar power system with a capacity of at least 1440 watts to meet your daily energy needs.
Keep in mind that this is a simplified formula and actual solar power system sizing may be more complex depending on factors such as panel efficiency, shading, and weather conditions. It's always best to consult with a solar professional to determine the exact size and type of solar power system that will meet your needs.
Subsidies for Solar Power Installation
Subsidies for solar power installation are available in many countries around the world. These subsidies are designed to incentivize the adoption of solar energy and to help make it more accessible to individuals and businesses.
In the United States, for example, the federal government offers a tax credit for solar power installations. This tax credit can cover up to 30% of the total cost of the system and is available to both residential and commercial properties. Some states and local governments may also offer additional incentives such as rebates or grants for solar power installations.
In India, the government offers a subsidy for solar power installations through the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. The subsidy is available for both grid-connected and off-grid solar power systems and can cover up to 30% of the total cost of the system. In addition to the subsidy, the Indian government also offers a range of other incentives such as tax exemptions and accelerated depreciation for solar power projects.
In Australia, the federal government offers a rebate for solar power installations through the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES). The rebate is calculated based on the size of the solar power system and can cover up to 30% of the total cost of the system. Some state and local governments in Australia may also offer additional incentives for solar power installations.
Solar Power Plant
A solar power plant is a large-scale facility that generates electricity from solar energy. Solar power plants can be either grid-connected or off-grid and can range in size from a few megawatts to several hundred megawatts.
There are two main types of solar power plants: photovoltaic (PV) solar power plants and concentrated solar power (CSP) plants.
Photovoltaic solar power plants use solar panels to convert sunlight directly into electricity. These plants can be ground-mounted, rooftop-mounted, or floating on water. They are typically more cost-effective for smaller-scale projects, but can also be used in larger utility-scale installations.
Concentrated solar power plants, on the other hand, use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area, which heats a fluid that then drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP plants can use various types of thermal energy storage to store excess energy generated during the day and use it to generate electricity during the night or on cloudy days. This makes them a good option for large-scale utility applications, as they can provide consistent power even when the sun is not shining.
Solar power plants can also have a significant positive impact on the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants associated with traditional fossil fuel power generation. They can also create jobs and stimulate economic growth in the communities where they are located.
However, the development and construction of solar power plants can also have potential environmental impacts, such as habitat fragmentation and land use changes. Careful planning and consideration of these impacts is important to ensure that solar power plants are developed in a sustainable and responsible manner.
Floating Solar Power Plant
A floating solar power plant is a type of solar power installation where photovoltaic panels are mounted on floating platforms on water bodies such as lakes, reservoirs, and ponds. This technology is gaining popularity in many parts of the world due to its many benefits.
Floating solar power plants have several advantages over conventional ground-mounted solar power plants. Firstly, they can help to save land and reduce land acquisition costs, as well as reduce water evaporation in reservoirs, thus conserving water. Secondly, the cooling effect of water can improve the efficiency of the solar panels, leading to increased power generation. Additionally, floating solar power plants can be built on existing water bodies, minimizing the need for land clearing and reducing environmental impacts.
One of the largest floating solar power plants in the world is the 150 megawatt plant located in Anhui, China. The plant consists of more than 166,000 solar panels mounted on 120,000 floats, covering an area of 1.14 square kilometers on a former coal mining area. The plant is expected to generate enough electricity to power 94,000 homes and reduce carbon emissions by 149,000 tonnes annually.
India's Largest Floating Solar Power Plant | Largest Floating Solar Power Plant In India
Conclusion
Solar power systems are a sustainable and renewable source of energy that can power your home or business while reducing your carbon footprint. There are different types of systems to choose from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a system, consider your energy needs, space availability, and budget. Installation and maintenance should be done by a professional to ensure safety and efficiency.
FAQs
How long do solar panels last?
Solar panels can last up to 25 years or more, but their efficiency will decrease over time.
Do I need batteries for a grid-tied solar power system?
No, batteries are not necessary for a grid-tied solar power system, but they can provide backup power in case of a power outage.
How much does a solar power system cost?
The cost of a solar power system depends on its size and components, but on average, it can range from $10,000 to $30,000.
Are there any tax incentives for installing a solar power system?
Yes, there are tax incentives available for installing a solar power system, including the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and state-level incentives. refer above article topic subsidy for detailed overview






Post a Comment